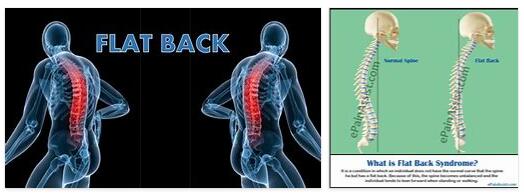
A flat back is a deformation of the spine in which it extends in a straight line from the topmost cervical vertebra to the pelvis. Normally the spine is subject to a natural curve with the purpose of cushioning our daily movements.
While there is a forward curvature in the cervical vertebra area, a backward curvature can be found in the thoracic vertebra area. In the lumbar region, the spine curves forward again in a healthy person, just like in the cervical region. Because of this lack of an S-curve, the flat back cannot take on the damping function. This leads to pain for those affected.
What is a flat back?
According to ACRONYMMONSTER.COM, a flat back is usually recognizable by an exceptionally straight posture and a stiffened neck. These characteristics are caused by the lack of or below average S-curvature of the spine, which in most cases mainly affects the lumbar area.
The flat back is particularly noticeable when lifting heavy objects. Here the pressure of the load can no longer be evenly distributed and the intervertebral discs and joints are overloaded.
The result is severe back pain. Children also suffer from this phenomenon very often. In addition to the main symptom, this can lead to back pain, listlessness, tiredness and irritability.
Causes
The causes of a flat back are diverse. On the one hand, this deformation can be triggered by incorrect posture. This happens particularly often during adolescence, as the spine is still growing during this period.
During this critical growth phase, a pathologically increased backward curvature of the thoracic column area or a hump can develop. The disease is also known as Scheuermann’s disease and can also be considered the cause of a flat back. Temporary posture errors in youth become permanent, as the spine orients itself in its further development to this wrong posture.
In addition, other diseases of the spine, such as rickets, lead to this phenomenon. This is a vitamin D metabolic disease that softens the bones and so the bones cannot withstand the daily stress. For example, they can be deformed in a straight line contrary to the natural S-curve. But surgical errors, such as the incorrect attachment of implants to the spine, can deform a healthy back in the direction of a flat back.
Symptoms, ailments & signs
Outwardly, a flat back appears to be flawless. The back is curved neither forwards (lordosis) nor backwards (kyphosis). However, the physiological S-shape of the spine is also missing, in which the thoracic vertebrae are slightly curved outwards and the lumbar vertebrae inwardly. A person who suffers from a flat back appears straight and stiff.
In the normally slightly curved spine, the forces are cushioned from top to bottom. This is particularly beneficial when carrying heavy loads. However, this cushioning does not apply to a flat back. Even when simply standing or walking, the full load of the upper vertebrae presses on the vertebrae below.
This leads to increased wear on the vertebral bodies. The high pressure on the lower vertebrae also prevents their optimal supply of nutrients. The result is severe pain, which is especially pronounced when lifting heavy objects. The pain with a flat back is comparable to the pain with pronounced kyphosis or scoliosis.
Without treatment, the vertebral bodies can rapidly wear out, with considerable impairment of mobility. In addition to back pain and restricted mobility, the affected patients often suffer from tiredness, listlessness and poor performance. The consequence of this is a deterioration in quality of life, which can also lead to depression and other mental illnesses.
Diagnosis
The flat back is in itself only a symptom. The diagnosis is made on the basis of an underlying disease, whereby other symptoms that occur should also be taken into account. In general, the person concerned has an exceptionally straight posture. This must be confirmed by the doctor with x-rays.
The next step is to determine the causes of this symptom. In addition to the causes already mentioned, such as rickets or errors in stiffening operations that have been carried out, intervertebral disc diseases or the atypical Scheuermann’s disease can also be triggers. In the case of diseases related to the intervertebral discs, the doctor should perform an MRI scan.
Complications
With a flat back, the patient suffers from relatively severe pain. These can occur either under stress or in the form of resting pain and severely limit the patient’s everyday life. As a rule, there is also a restriction of movement and thus a decrease in the quality of life. In many cases, those affected also complain of tiredness and listlessness.
It is not possible to compensate for tiredness with enough sleep, so that the patient feels weakened and has a general feeling of illness. Children can also suffer from a flat back and are therefore restricted in their physical development. The pain usually has a negative effect on the psyche, so that most of those affected also suffer from depression and other mental complaints.
The pain usually also leads to increased irritability and aggressiveness. These factors can have a negative impact on the environment and on social contacts. The treatment of the flat back is usually carried out with the help of various exercises.
There are no further complications. In serious cases, surgical interventions can be carried out. The course of the disease is usually positive and does not affect life expectancy.
When should you go to the doctor?
Treatment for flat backs is not always necessary, but should still be carried out in order to avoid further complications and complaints in the everyday life of the person concerned. The patient should always consult a doctor with this disease if there is severe back pain in everyday life.
These occur mainly when lifting heavy objects or during everyday movements. Should this pain occur without a particular reason and, above all, permanently, a visit to a doctor is definitely necessary.
The back loses its typical S-shape, so that the person concerned suffers from a stretched back. A visit to a doctor is always necessary with this complaint. The diagnosis and treatment of the disease can be done by an orthopedic surgeon or by a general practitioner.
In some cases, however, those affected need surgery to alleviate the symptoms. Various exercises and therapies can also help alleviate the symptoms of this disease. Early treatment increases the likelihood of a positive course of the disease.
Treatment & Therapy
Appropriate therapy can only be given after the causes of the flat back have been clarified. The flat back can usually be identified as a symptom of another underlying disease. Or it is a result of a bad posture during adolescence.
Surgery is rarely done for treatment. The exception to this is a secondary change in the intervertebral discs and joints that has already occurred, whereby damaged intervertebral discs are surgically removed and the spine can be corrected and stabilized with metal plates and screws.
These surgical interventions are only carried out if there is a pronounced flat back. Long-term therapy is also often not necessary for a flat back. Usually a few balance and equilibrium exercises on an uneven surface are enough to restore the spinal balance.
The patient learns to control his posture and the muscles are also strengthened. This also preserves the mobility of various spinal column sections, so that stiffening of the body is avoided. In the case of acute complaints, conservative treatment methods such as physiotherapeutic treatment according to Brugger are used. In this holistic therapy on a neurophysiological basis, individual functional disorders of the movement system are analyzed and the pain and disruptive factors are treated.
But also stretching exercises of the thigh muscles or a compensation of the muscular imbalance in the hip, lumbar and pelvic area can represent treatment methods for the diagnosis of flat backs. However, if the flat back remains untreated for a longer period of time, it will be difficult to restore the normal curvature approximately through simple exercises.
Outlook & forecast
The prognosis of the flat back depends on the extent of the symptoms and the underlying disease. Those affected who do not suffer from any other impairments such as pain or restricted mobility have a good prospect.
In most cases, the health of these patients is stable and will cause few problems over their lifespan. If the flat back has arisen due to postural damage, the time of diagnosis and the intensity of the damage are decisive for the healing process. The younger the person is and the smaller the defect, the more likely it is that their health will improve.
Symptomatic relief can be achieved with targeted training and exercise units. Freedom from symptoms is entirely possible with good cooperation from the patient. In some cases, surgery is required. Here, the prognosis is made individually and depending on the damage present.
The aim is to reduce the symptoms and thus optimize well-being. A cure is not always achieved. Many patients have to complete lifelong stretching exercises and other physical therapy training in order to maintain their health and at the same time counteract deterioration.
In the case of a metabolic disease or surgical errors, the prognosis must be assessed according to the individual circumstances. There are good treatment options for both that lead to improvement or recovery.
Prevention
In order to prevent a flat back, it is advisable to train the back and abdominal muscles regularly with suitable exercises such as torso lift, front support or iso-crunches. In addition, correct posture, whether sitting or standing, should be ensured through educational measures. Suitable seating furniture, especially in the office, can support this in a positive way.
Aftercare
In many cases, the flat back is so pronounced that it cannot be brought into the physiologically correct shape. That is why aftercare is to be seen as a lifelong process, where measures are taken that optimally counteract the flat back. The right people to talk to are the family doctor and the orthopedic surgeon, but support from physiotherapists is also helpful.
Specialized sports therapists and rehab sports teachers are also the right address for flat backs. Because targeted training is the measure that is particularly important in connection with the measure for flat backs. The aim is to bring the flat back as close as possible to the normal S-shape of the spine. This can often be best achieved through regular strength training.
The core muscles of the abdomen and lower back must be strengthened as well as the chest muscles and the muscles of the upper back. Targeted stretching training is also important. Here, shortened muscles such as the back of the thighs or the chest are gently stretched.
The shoes are also important in the context of aftercare. Because if the S-shape of the spine is not as pronounced as it should be due to the flat back, the natural buffer function is missing. Padded shoes offer additional protection for the intervertebral discs. Walking barefoot helps to strengthen the arches of the foot and also absorbs bumps well.
You can do that yourself
To combat the flat back, there are a few simple exercises that are easy to incorporate into everyday life. In the first exercise, the person concerned gets on their knees and hands and lets the part of the back sag where the curvature of the spine is absent. This improves the mobility of the spine. This position is held for between two and two and a half minutes. Cushions under the hands help to relieve the arms.
For the second exercise, the person sits on their heels. Then she lowers her upper body until her forehead touches the floor. You should now feel a back curve in the thoracic spine area. The position is held for two minutes.
The third exercise against the flat back begins as in the second. In the heel seat, the head is overstretched backwards. The hands help with gentle pressure on the forehead. On the front of the body, this two-minute exercise stretches what is in the way of the curvature of the spine. The fourth exercise is to overstretch the head while lying down with a medi roll in the neck.
With these exercises, life with a flat back can be made easier in everyday life. They can be carried out quickly and easily and are not dangerous. It is only important to slowly loosen the position of an exercise so as not to damage the muscles. If problems arise or support is required, it is advisable to consult a physiotherapist.