The jugular foramen syndrome is also known as Vernet syndrome and corresponds to a failure of the three cranial nerves IX, X and XI, which manifests itself in symptoms of dysphonia and dysphagia. Usually the cause is a tumor in the middle area of the jugular forman. The treatment is carried out by means of excision, since radiation therapy in this area has proven to be particularly harmful.
What is Jugular Foramen Syndrome?
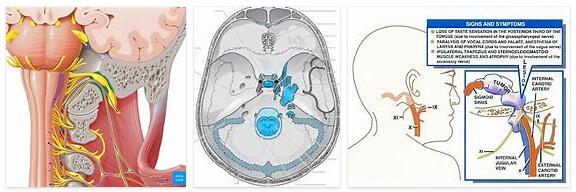
According to WHICHEVERHEALTH.COM, the jugular foramen is also known as the throttle hole and corresponds to a large opening in the area of the skull base through which the nerve pathways descend to the neck area. The anatomical structure is located behind the exit of the internal carotid artery. The anterior border of the area is formed by the petrous bone. The posterior border represents the occiput.
Overall, the jugular foramen consists of three different compartments. The anterior parts are called the anterior pars and contain the inferior petrosal sinus. The middle part is called the pars intermedialis and is home to the cranial nerves IX, X and XI with the glossopharyngeal nerve, the vagus nerve and the accessory nerve.
In addition, the posterior meningeal artery, which supplies blood to the meninges, is located in this section. The last compartment corresponds to the pars posterior, which is home to the sigmoid sinus. The jugular foramen syndrome is a complex of symptoms preceded by damage to the anatomical structure.
The main symptom is a partial or complete failure of the cranial nerves IX, X and XI. The clinical picture is also referred to in the specialist literature as Vernet syndrome. This name goes back to the person who first described the disease: the French neurologist Maurice Vernet, who documented the syndrome at the beginning of the 20th century.
Causes
Vernet syndrome is caused by damage to the jugular foramen. The middle part of the anatomical structure is particularly important in this context, as the three cranial nerves come through the shaping at this point. The primary cause of the impairment of the cranial nerve structure can be traced back to a glomus tumor, for example.
This cause is the most common. The glomus tumor corresponds to a paraganglioma, which is usually benign and neuroendocrine in nature. Such tumors arise from autonomic ganglia originating in the parasympathetic or sympathetic nervous system.
Meningiomas or schwannomas such as acoustic neuroma can also be involved in the development of a jugular foramen syndrome. Other possible causes are metastases within the cerebellopontine angle. The syndrome is rarely caused by cholesteatomas or is due to mechanical damage after trauma.
Symptoms, ailments & signs
Patients with jugular foramen syndrome show varying degrees of cranial nerve failure. As a rule, it is not partial, but total failures that cause complete paralysis in the motor supply area of the cranial nerves. Such paralysis manifests itself in detail as dysphonia, for example in the form of pathological hoarseness.
Equally common are symptoms such as dysphagia or sensory disorders and sensory disorders in the back third of the tongue. In the case of sensory disorders, patients often recognize tastes as bitter, among other things, even though the food consumed is not a bitter food.
In addition to the symptoms mentioned, paralysis of the affected soft palate side often occurs, which causes a deviation from the healthy side. In many cases, the parotid secretion decreases bit by bit. Due to the sensitivity and sensory disorders, the gag reflex can also experience impairments. In addition, failures of the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles often occur.
Diagnosis & course
The diagnosis of Vernet syndrome is usually made on the basis of the clinically characteristic criteria. The first suspicion can be confirmed by imaging of the skull. The MRI is particularly suitable in this case.
Causal tumors show a typical picture in the slice images and thus allow classification as foramen jugular syndrome. The prognosis for patients with Vernet syndrome depends primarily on the degree of malignancy. Operability can also have a decisive impact on the prognosis.
Complications
In the jugular foramen syndrome there are various complications that depend on the affected region in the brain. In most cases, the failure of the brain nerves leads to paralysis, disabilities and other disorders in the body. Sensitivity disorders occur more frequently, which can have a strong influence on the patient’s everyday life.
In many cases, the perception of taste is also disturbed, with foods sometimes tasting more bitter than they actually are. The sensory system and the movements of the muscles are also disturbed due to the jugular foramen syndrome. Complications mainly occur when the cranial nerves have been permanently damaged.
It is not possible to restore the damaged nerves and the patient has to live with the complications that arise. If the nerves have not yet been damaged and the tumor can be removed successfully, there will be no complications. Chemotherapy is also used in many cases.
In the case of a benign tumor, treatment is not absolutely necessary. Treatment is often foregone as long as there are no complications. Foramen jugular syndrome reduces life expectancy when the tumor spreads in a malignant form. In the worst case scenario, this can lead to death.
When should you go to the doctor?
Since the jugular foramen syndrome does not heal itself and in most cases the symptoms worsen, a doctor must always be consulted. A visit to the doctor should be made if the person concerned suffers from paralysis or chronic hoarseness. The paralysis occurs mainly in the face or mouth and on the tongue and can lead to difficulty swallowing or to discomfort when ingesting food.
In many cases, even a bitter taste in common foods can indicate jugular foramen syndrome, so a doctor examination is necessary. Many people affected by foramen jugular syndrome also suffer from a pronounced gag reflex, so that they vomit frequently. Foramen jugular syndrome can be diagnosed with a general practitioner or with an ENT doctor.
Further treatment, however, always depends on the underlying disease, with a complete cure in many cases not being possible. In the case of psychological complaints or depression, a psychologist should always be consulted, as a healthy psyche can also accelerate the healing process. Psychological treatment may also be necessary for the patient’s parents or relatives.
Treatment & Therapy
The Vernet syndrome is usually treated causally. Causal therapy starts with the primary cause of the failure symptoms and tries to resolve the primary cause. With the elimination of the primary trigger, the individual symptoms also subside, as long as the cranial nerves have not suffered any irreparable damage from the tumor.
Smaller impairments can nonetheless remain even after the causative tumor has been eliminated. The therapy of choice is a more or less complete excision of the tumor. The surgical removal of intracranial glomus tumors is particularly difficult because of the abundance of blood and the infiltrative growth of the tumor type.
As an alternative to invasive procedures, radiation or chemotherapy can be used. However, these forms of therapy are considered controversial in the context of foramen jugular syndrome. The cranial nerves suffer irreparable damage, especially during radiation therapy in this area.
If the tumor is benign, the benefits of each therapy must be weighed against the expected risks. Benign tumors in the area of the jugular foramen do not necessarily have to be removed. If the tumor causes hardly any symptoms, in this case at least a wait-and-see attitude can be adopted so as not to risk an unnecessary worsening of the symptoms.
Outlook & forecast
The prognosis of the jugular foramen syndrome is tied to the cause of the disorders present and the treatment options that can be used. If the failure of the cranial nerves at the foramen is caused by a tumor in the brain, the patient may die prematurely in the worst case.
Depending on the location of the tumor, a decision is made as to whether a surgical procedure and cancer therapy can be carried out. In the case of a benign tumor that can be completely removed without further complications, the patient has the prospect of a cure. If there are no other impairments, the person concerned is considered to have recovered after the follow-up treatment. Check-ups will be carried out at regular intervals in the coming months and years. If no new tissue changes form, the patient is considered to be permanently cured.
If there is a malignant tumor disease, the chances of recovery deteriorate immensely. If further growth cannot be prevented despite irradiation of the tumor, there are no prospects for a cure with the current medical possibilities. Metastases develop and the cancer gradually spreads.
If the jugular foramen syndrome is triggered by a fall or accident, the prognosis must be assessed according to the extent of the damage to the skull. Repair is possible in the case of minor defects or cracks. Large-scale damage, on the other hand, leads to lifelong impairment.
Prevention
The jugular foramen syndrome cannot be prevented. The tendency to develop paragangliomas lies in the genes, since the tumors have been associated with familial accumulation in the past. The only preventive measure in this case would be that patients with a known propensity for the tumor type do not have children of their own.
Aftercare
In most cases, aftercare options are not available to those affected by foramen jugular syndrome, or only to a very limited extent. Since this is a genetically determined disease that is inherited, only symptomatic therapy, rather than causal, can be carried out. A full recovery is not possible.
If you want to have children, a genetic test can also be carried out in order to prevent the foramen jugular syndrome from being passed on. In most cases, treatment is carried out with the help of medication. The patient is primarily dependent on the correct and regular intake of the medication in order to permanently alleviate the symptoms.
Since the jugular foramen syndrome also leads to the appearance of various tumors, regular examinations should be carried out by a doctor in order to detect the tumors at an early stage and also to remove them. Self-healing cannot occur in the jugular foramen syndrome.
The intensive and loving care of the person concerned also has a positive effect on the further course of the disease, whereby these are often dependent on intensive discussions in order to prevent psychological upsets or depression. The life expectancy of the person affected may be reduced by the disease.
You can do that yourself
In the event of a failure of the cranial nerves, the person affected has few options to bring about an alleviation or cure of the disease through their own efforts.
The patient will help himself the most if he or she has foramen jugular syndrome consulted professional doctors whom he trusts and with whom he can work well. It is important and very helpful if the sick person is fully informed and cleared up about the disease. This is helpful in managing the symptoms in everyday life.
Even if the possibilities for improving the situation are limited on the physical level, the person concerned can take care of his or her psychological stability. A positive outlook on life and optimism favor the time during medical treatment and the subsequent healing process. With a stable social environment at his side, the sick can draw new strength and gain confidence in difficult phases.
If the emotional problems increase, it is helpful to see a therapist. The way of life should be designed in such a way that well-being and joie de vivre arise. Despite changed or limited design options, there are different approaches to leisure planning that can be used according to individual preferences. This brings new drive and has a positive effect on general health.