About Fibromyalgia
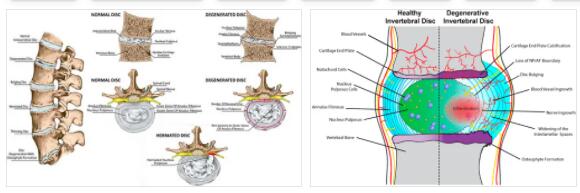
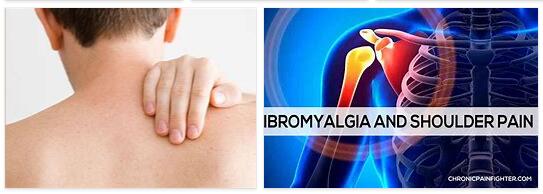
The fibromyalgia or fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) is a disease characterized by severe pain is characterized throughout the body. The causes have not yet been researched and treatment is primarily aimed at relieving the symptoms. Fibromyalgia is currently not curable, but the severity of the symptoms can weaken with age. What is fibromyalgia? According to FOODEZINE.COM, fibromyalgia, also known as fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS), is a disease that causes pain in muscles, tendons and bones. Usually other diseases are initially suspected, such as rheumatism or back damage. Fibromyalgia is a generalized disease, which means that it not only causes discomfort in certain areas or a few parts of the body, but affects the entire body. Fibromyalgia usually spreads symmetrically. Patients experience muscle pain in particular, but generally have a lower pain threshold.…