About Fitz Hugh Curtis Syndrome
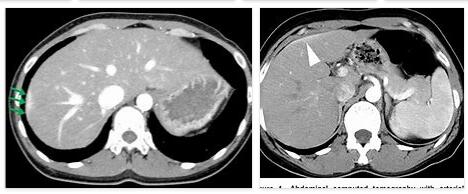
The Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome, short FHC syndrome occurs predominantly as a complication after an inflammation of the pelvis on. Abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting occur. What is Fitz-Hugh-Curtis Syndrome? According to USVSUKENGLISH.COM, the disease was first noticed by a Uruguayan surgeon in 1920. It was first described by the American gynecologist Arthur Hale Curtis. In 1934 an American internist was able to confirm Curtis' observations. Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome is therefore a complication of a previous inflammation of the pelvis. In most cases this is caused by chlamydia or other bacteria and leads to inflammation in the liver and diaphragm. The Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome is therefore also known as perihepatitis. Causes Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome is a complication of an ascending bacterial infection of the female genital area. The disease is often caused by chlamydia or…